-
Japanese / English





Requesting Strains, F1 Hybrids, Transgenics, Mutants
In this project, we provide the embryos, larvae, metamorphosed juveniles and adults of X. tropicalis as research resources. The living resources maintained at this resource center are roughly classified as follows. There is a list of living resources currently available at the bottom of the page. You can also select a derived lineage on the detail page.
-
•Inbred strains
-
•F1 hybrids between the inbred strains
-
•Transgenics
-
•Mutants
Advantages of hybrid frogs
We have maintained healthy inbred individuals after more than ten generations of sibling-matings. These resources are genetically and physiologically homogeneous and should be useful for genetics and genomics. However, hybrids of the different inbred strains are more robust and genetically homogeneous at colony level (= among individuals).
Search for X. tropicalis Living Resources
-
09-01-2020
-
Prices have been revised due to the increased costs associated with breeding and packaging. This revision includes the increase in the sales tax rate.


Type: Wild type. Genetic Modification: Unaltered.
RRID: HUARC_1001. Xenbase Identifier: XB-LINE-1147.
This strain originated from a Nigerian strain maintained at the Grainger lab (University of Virginia, USA). Dr. Asashima (The University of Tokyo, Japan) obtained the sixth generation of the Nigerian A2 strain used for genome sequencing by JGI from Dr. R. Grainger in 2003. This strain was propagated to the eleventh inbred generation in his laboratory and provided to the Amphibian Research Center in 2014.
Reference: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26222540


Type: Mutant. Genetic Modification: Modified artificially.
RRID: HUARC_2004. Xenbase Identifier: XB-LINE-2058.
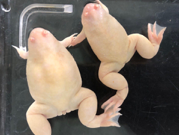
An albino line with CRISPR/Cas9-targeted mutation in tyrosinase (tyr) gene, made by the Ochi Lab. The target sequence is in exon 1 [GGAAAGGAACATGGTCCCTC].
Refereence: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/27219625/






Type: Wild type. Genetic Modification: Unaltered.
RRID: HUARC_1002. Xenbase Identifier: XB-LINE-1153.
This strain originated from frogs Dr. K. Yasuda (NAIST, Japan) obtained from the Grainger lab (University of Virginia, USA) in 1996 and propagated for several generations. The eighth generation was provided to the Amphibian Research Center in 1998 and 2003. This strain was previously labelled as “Yasuda” and renamed because its mitochondrial haplotype is identical to Nigerian.
Reference: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26222540
Type: Wild type. Genetic Modification: Unaltered.
RRID: HUARC_1003. Xenbase Identifier: XB-LINE-1163.
This strain was previously labelled as “Golden” and originally came from a stock maintained by Dr. E. Amaya at the Univeristy of California, Berkeley and subsequently maintained for a short period by Dr. T. Hyaes. The Golden strain was developed by artificial selection for fast growth and rapid sexual maturity in the Harland lab. Dr. M. Asashima (The University of Tokyo, Japan) obtained this strain from Dr. R. Harland in 2005 and provided to the Amphibian Research Center in 2009 and 2010.
Reference: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26222540

Type: Wild type. Genetic Modification: Unaltered.
RRID: HUARC_1004. Xenbase Identifier: XB-LINE-1160.
This strain was taken from a wild population in Adipodoumé, Ivory Coast, and has been shown to be diploid (Tymowska & Fishberg, 1973). Adult males and females were provided to Dr. K. Yoshizato (Institute for Amphibian Biology, Hiroshima University) in 1998 from Drs. D. Rungger and H.R. Kobel at Université de Genève.
Reference: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26222540

Type: Wild type. Genetic Modification: Unaltered.
RRID: HUARC_1005. Xenbase Identifier: XB-LINE-2054.
A strain branched from the 5th generation of Xtr.NigerianBHHuarc. This strain will be maintained without reducing heterozygosity.
Reference: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26222540
Type: Wild type. Genetic Modification: Unaltered.
An F1 hybrid between Xtr.NigerianHHuarc and Xtr.NigerianBHHuarc.
Reference: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26222540
Type: Mutant. Genetic Modification: Modified artificially.
RRID: HUARC_2003. Xenbase Identifier: XB-LINE-2057.
An albino line with CRISPR/Cas9-targeted mutation in tyrosinase (tyr) gene, made by the Suzuki Lab. Animals have a 4-bp deletion in exon 1 [CCTGTTCTTCTTCCTCCA----TGCAGGGGCCAGTTCCCA].
Refereence: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/27219625/

Type: Mutant. Genetic Modification: Modified artificially.
RRID: HUARC_2002. Xenbase Identifier: XB-LINE-2056.
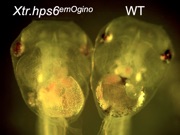
CRISPR/Cas9-mediated targeted mutation in hsp6, a gene resonsible for X. tropicalis no privacy (nop) mutant and human Hermansky-Pudlak Syndrome, made by the Ogino Lab.
Reference: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/27595926/

List of X. tropicalis living resources
Ordering systems were constructed by the department of NBRP Information.






Type: Wild type. Genetic Modification: Unaltered.
An F1 hybrid between Xtr.NigerianAHuarc and Xtr.NigerianHHuarc.
Reference: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26222540










Type: Transgenic. Genetic Modification: Modified artificially.
RRID: HUARC_3001. Xenbase Identifier: XB-LINE-2059.
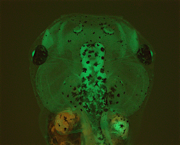
A X. tropicalis Tg line carrying a neuron-specific beta-tubulin (tubb2b) promoter driving EGFP expression, made by the Ogino Lab.
Reference: Sakagami, K., Igawa, T., Sakaguchi, Y. et al., in preparation.



Type: Transgenic. Genetic Modification: Modified artificially.
RRID: HUARC_3003. Xenbase Identifier: XB-LINE-2061.
A X. tropicalis Tg line carrying a CMV promoter driving ubiquitous EGFP expression, made by the Ogino Lab.
Reference: Unpublished.
Type: Transgenic. Genetic Modification: Modified artificially.
RRID: HUARC_3002. Xenbase Identifier: XB-LINE-2060.
A X. tropicalis Tg line carrying a X. laevis ubiquitos EF1a (eef1a1) promoter driving human Histone 2B fused to EGFP, made by the Ogino Lab.
Reference: Unpublished.

Type: Transgenic. Genetic Modification: Modified artificially.
RRID: HUARC_3004. Xenbase Identifier: XB-LINE-2062.
A X. tropicalis Tg line carrying a myf5 promoter driving EGFP expression in somite, made by the Ogino Lab.
Reference: Unpublished.



Type: Mutant. Genetic Modification: Modified artificially.
RRID: HUARC_2001. Xenbase Identifier: XB-LINE-1859.
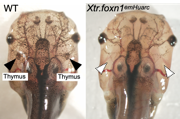
An athymic line with TALEN-mediated targeted mutation in foxn1 gene, made by the Yaoita Lab. Absence of immunological rejection and useful for tissue transplantation experiments.
Reference: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26847415/








Type: Wild type. Genetic Modification: Unaltered.
An F1 hybrid between Xtr.NigerianAHuarc and Xtr.NigerianBHHuarc.
Reference: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26222540


-
‣ Xenopus tropicalis
Copyright Ⓒ NBRP X. tropicalis. All rights reserved.